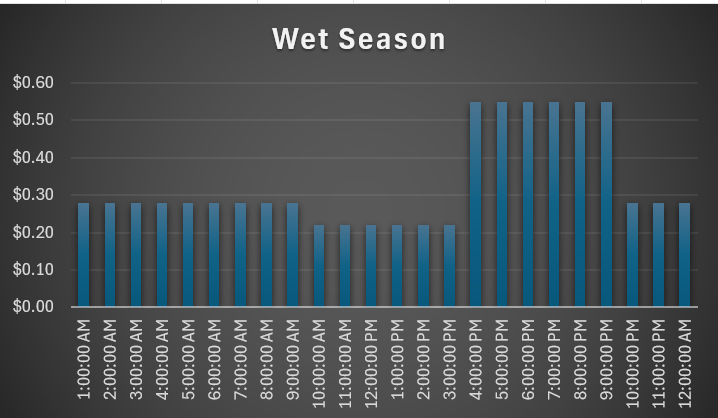
Why now might be the best time to buy a home battery
Simplifying the New Solar Installation Standard (AS/NZS 5033:2021) for You
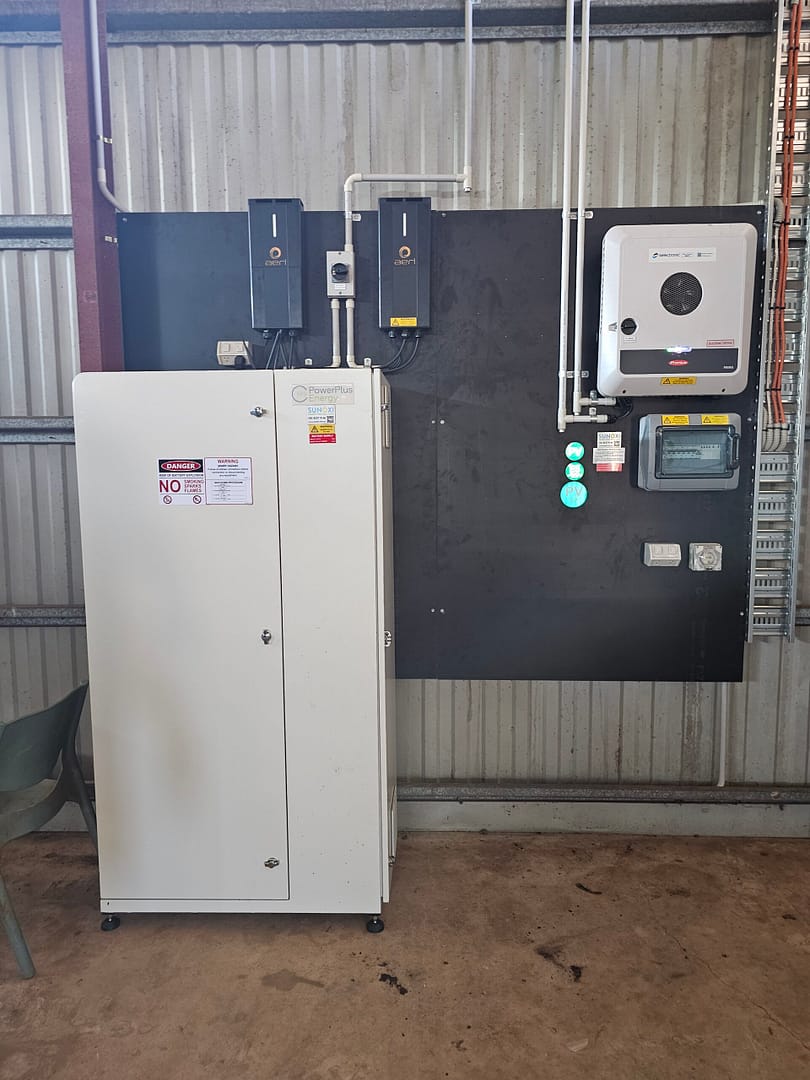

Off grid systems supply electricity to properties that are not connected to, or have chosen to disconnect from, the local electricity network.
Solar panels convert sunlight to direct current (DC) electricity, which is then fed through the solar inverter to create usable alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is then sent to the switchboard, where it is sent to the household appliances that are using electricity at the time, and any surplus electricity is sent to the battery bank to recharge it.
The inverter/charger will stop the solar system from recharging the batteries once they are full. When your solar system is not producing electricity, your battery bank will send power to your household appliances.
If the battery bank state-of-charge level gets too low, the inverter/charger will turn on the backup generator automatically to power the house electrical appliances and recharge the battery bank.
There are two different ways of configuring an off grid system – AC-Coupling and DC-Coupling – and each have unique advantages. The configuration type will have an impact on the life expectancy, efficiency and flexibility of your system.
Just like yourself, they have installed solar Inverters and solar battery storage at their homes to fight against the rising costs and help to decarbonize our society.
Contact us today for an obligation free assessment of your business’ particular solar system needs.

Simplifying the New Solar Installation Standard (AS/NZS 5033:2021) for You

Simplifying the New Solar Installation Standard (AS/NZS 5033:2021) for You
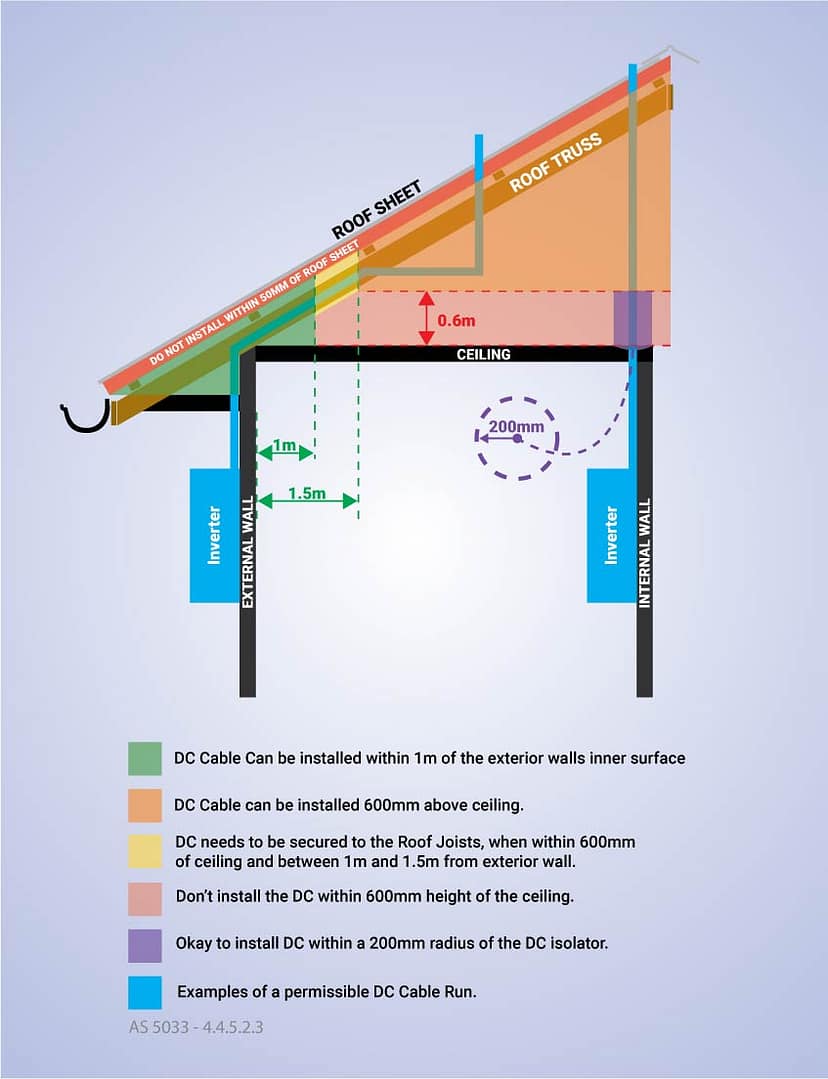
Simplifying the New Solar Installation Standard (AS/NZS 5033:2021) for You
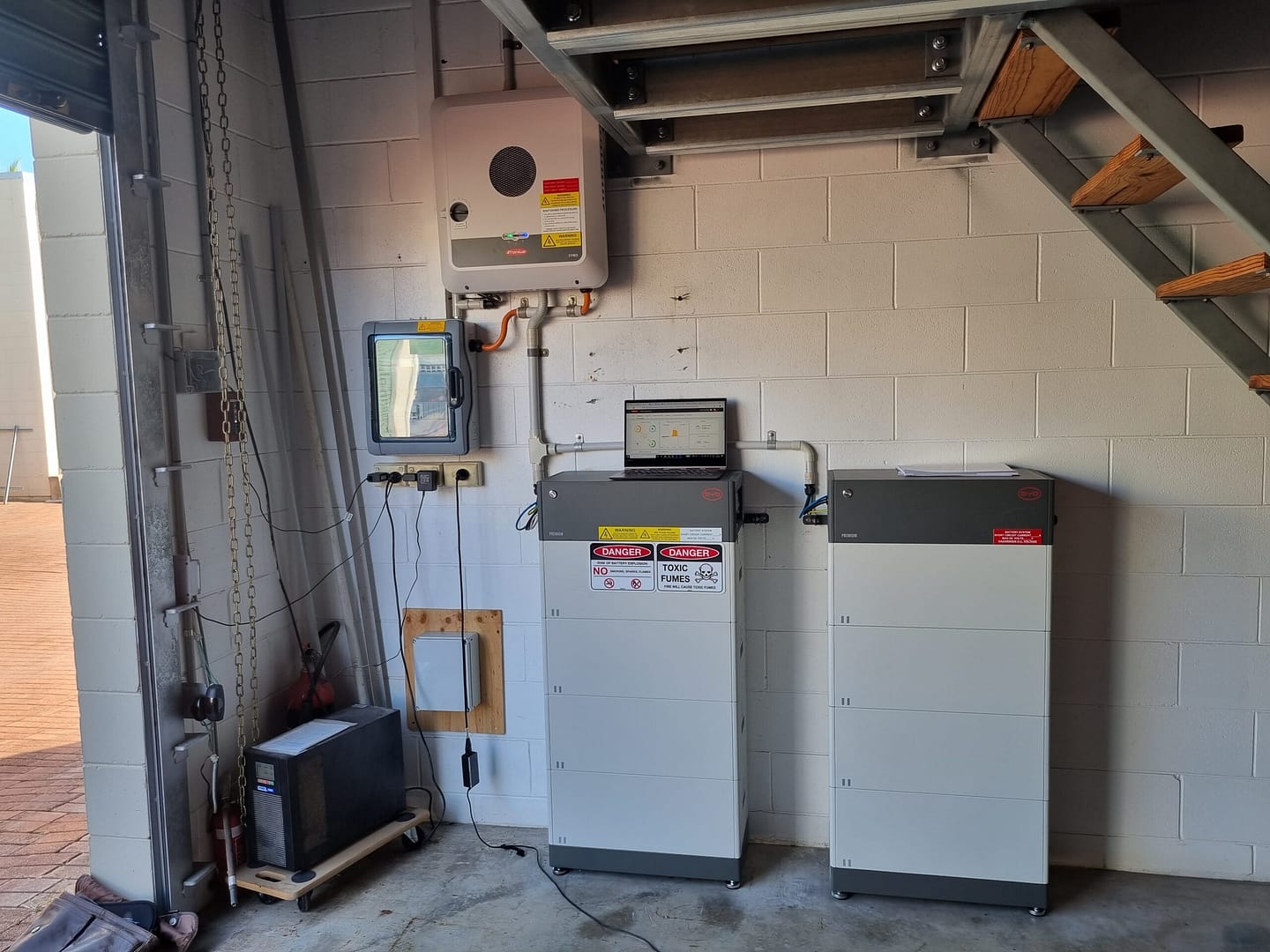

THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN AN AC & DC COUPLED SOLAR BATTERY